At Import
Standards are used to define the drawing representation to which DXF/DWG data are imported, as well as mapping DXF/DWG attributes.
- Drafting
- The imported data are put in a
drawing representation. This drawing representation uses styles defined in a
pre-defined or a customized standard such as ISO, JIS, ANSI, ASME. The
Drafting list
lets you select this standard.
- The content of this list depends on which
standards have been created and/or customized by your administrator.
- The most suitable format (A0 ISO, A1 ISO, etc.)
for each sheet (layout) is automatically determined, i.e. the smallest format
in which the drawing can be totally included is selected.
- If the standard is ISO, the format is chosen
among A0 ISO, A1 ISO, A2 ISO, etc.
- If the standard is ANSI, the format is chosen
among A, B, C, etc.
- If no standard format fits the sheet, the
format is set to the largest one i.e. A0 ISO and made invisible with a message
"No standard format can be applied to this sheet" in the report file.
- In export/import loops, the automatic
determination of the standard may lead to format changes.
- If you are not satisfied with this automatic
result, use the Page Setup command to modify the format.
Information on what has been determined automatically
is written in the report file.
For more details about standards, see
Administration in the
Drafting
User's Guide.
-
DXF
-
Some AutoCAD attributes do not exist in 3DEXPERIENCE as such and require a
mapping:
- AutoCAD color can be mapped to 3DEXPERIENCE line thickness.
- AutoCAD line type is mapped to 3DEXPERIENCE line type.
- AutoCAD text font is mapped to 3DEXPERIENCE text font.
- AutoCAD layers can be mapped to specific 3DEXPERIENCE layers.
These mappings are defined in a DXF standard file, which you can
select from the DXF list. The content of this list depends on which standards have been
created and/or customized by your administrator.
At Export
The export section of the standard file defines the mapping of patterns between 3DEXPERIENCE and DXF.
Information about the export of patterns is given in the report file.
About DXF Standards
Standards are defined by your administrator in XML (Extensible
Markup Language) files to set default values for element
properties.
- The elements used in the mappings customized in the DXF
standard are those defined in the Drafting standard. This ensures
the consistency between the DXF/DWG interface and the
drawings.
- Standard files apply to all the sessions using them,
thus controlling the company standard at the import process.
- The DXF.xml file is a standard that sets the default mapping
between DXF/DWG and Drafting elements, for the color to thickness, line
types and text fonts.
- The DXF.xml file is stored under
installation_folder\resources\standard\dxf.
For multi-sites installations,
we recommend that the administrator loads the DXF.xml file in Data Setup, thus making sure one single standard file is
available for all users in on-line mode. For more information, see About Data Setup for Drafting.
- The USED MAPPINGS section of the report file lists
the associations used during import.
You
can use the default mapping found in the standard file provided in your installation, customize it, or create new standard files to meet your
needs. When several standard files exist, you can select one.
Structure of the Standard
The structure of the standard is defined by the administrator.
A standard file is structured as a tree, as it appears in the
Standards Editor
(available via ).
It contains several main sections, each dealing with a specific
aspect of the customization.
Description of the Standard Parameters
All the parameters are in DXF Import, under dxf Category.
- Line Type Mapping
- Associates a Drafting line type for any given DXF line
type:
- Select the DXF line type by its name.
- Select the Drafting line type by its number.
If a name of line type found in the DXF file is not present in
the list, the default Drafting line type will be applied to the imported
entity.
- Color To Thickness Mapping
- Associates a Drafting line thickness for any given DXF
color. This capability is useful for DXF files up to the version
AutoCAD-R14 in which the line thickness was not defined, and for
which the color may be used to define a line thickness.
- Select the DXF color by its number.
- Select the Drafting line thickness by its number.
- Text Font Mapping
- Associates a Drafting text font for any given DXF text
font:
- Select the DXF text font by its name.
- Select the Drafting text font by its number.
- Associate a X scale factor to reframe a font with a different
geometry (characters too wide or too narrow) to achieve the best
possible alignment.
- Define a default font to be used when there is no mapping for a
DXF font.
- Define a default KANJI font, other than SSS4, to be used when
the BigFont DXF font is not mapped.
If a name of text font found in the DXF file is not present in
the list, the given default Drafting text font will be applied to the
imported text.
- Thick Polyline Mapping
- Controls the way polylines with adjustable width are
imported. Those polylines do not use the standard lineweight attribute,
but use either Constant width attribute, or Start
segment width and End segment Width for each
vertex of the polyline. They can be imported as lines and arcs or
as area fills depending on the value of CreateAreaFill
and MinThicknessForAreaFill in the
ThickPolylineMapping standard.
When the width of the polyline is not null:
- CreateAreaFill=yes authorizes the area fill
creation.
In this case, if width is greater than the value of
MinThicknessForAreaFill, an area fill that represents
the exact geometry of the thick polyline is created.
- CreateAreaFill=No, or if width is lower than the
value of MinThicknessForAreaFill, the lines and arcs are
created with a line thickness mapped from the polyline width.
The value taken for the width is the greater one of
startWidth or endWidth for each segment of
the polyline.
The report file indicates: - Whether a thick polyline mapping has been
applied during the import of the DXF file.
- How the thick polylines are
mapped.
Limitations:
- When an area fill is created, the line type of the polyline is
not taken into account. This applies only when the width is greater
than the value of MinThicknessForAreaFill given in the
DXF standard.
- When no area fill is created, in the case of polyline with
constant width, arcs or lines will be created for each segment, but
no Drafting polyline.
- Color Mapping
- Controls the adaptation of Black and
White colors to the background color:
- By default, the sheet background is dark blue in 2D Layout for 3D Design, since it is white in Drafting. The consequence is that black lines that are the most frequent in
DXF files are not, or only hardly visible.
- To improve the visibility of the result of the import in
2D Layout for 3D Design, a new section Color
mapping is added in the DXF standard file with three
parameters:
- Adapt to Background
- Yes (default value): the Black and
White colors will be changed, either to black or to
white depending on the background color and the second
parameter.
- No: the White and Black colors
from DXF will not be changed: they may be not or almost not
visible.
- Dark background luminosity (0..255)
- If Adapt to Background=No: this parameter has no
effect.
- If Adapt to Background=Yes: this parameters defines
at which luminosity value of the background the Black
color is switched to white:
- If the background luminosity is lower than the given value, that
means the background is dark and the Black color from
DXF will be changed to white.
- If the background luminosity is greater than the given value, the
Black color from DXF remains black.
The proposed Dark background luminosity (0..255) is 100. - Light background luminosity (0..255)
Notes:
- Dark background luminosity and Light background
luminosity should be between 0 and 255.
- Dark background luminosity must be lower than or
equal to Light background luminosity. If it is not the
case the Light background luminosity is set to Dark
background luminosity.
- When a change of Black or White color is
done during the conversion because of the Adapt to
Background mapping, the information is given in the report
file of the DXF conversion.
- When the DXF standard does not contain these parameters, the
default values are taken. The report file indicates if the
adaptation to background color has been applied during the import
of the DXF file.
- Pattern Mapping
- Defines a mapping between a Drafting image representing a pattern and a DXF pattern, when exporting data from Drafting to DXF.
This mapping is required because the representation of a pattern is
different in DXF and Drafting:
- An area fill is defined by one external contour and several internal contours
in both DXF and Drafting. The graphic representation in these contours allows to schematize
materials.
- For DXF, this graphic representation is defined by:
- A pattern made of lines
- Or a pattern coloring gradient.
- In Drafting, this graphic representation is defined either by:
- A pattern hatching (several lines with type, color and maximum number)
- A pattern dotting (point with pitch and color)
- A pattern coloring (color)
- Or a pattern image (image with scale and angle).
For example, in Drafting concrete is represented by an image, whereas it is represented by a pattern
made of lines in DXF. In such cases, you can map the image with a DXF pattern in the
standard file.
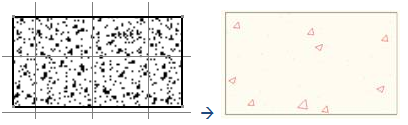
Once you have selected a Drafting pattern image, you can define its DXF properties on the right side of the
dialog box.
- Layer Mapping
- Defines a mapping between imported layers and 3DEXPERIENCE layers.
- The name of the imported layer is mapped with a 3DEXPERIENCE number and a 3DEXPERIENCE layer name.
- If the name of an imported layer has no mapping, the layer is created as new.
- You can use the character * to replace any character in the imported layer name. This way, you can assign several imported layers with different names to one 3DEXPERIENCE layer.
|
