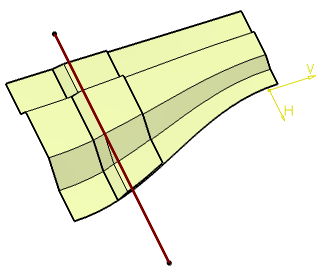
Creating a Mating Flange | |||||
|
| ||||
-
From the
Automotive
section of the
action bar, click Mating Flange
 .
.
- In the Base surface box, select a surface.
It can have several faces and internal sharp edges.
- In the Reference element box, select a reference element to position the
mating flange on the base surface.
It can be:
- a plane or a surface. The reference location is computed as an intersection with the base surface.
-
a curve (as in our scenario): the curve can be either a 3D curve or a planar curve and must have a projection on the base surface along the reference direction.
Tip: We advise you not to use the intersection or projection curve but rather the input surface or curve. - In the Reference direction box, select a direction.
Tips: - To select a default reference direction, right-click in the box and select the Default Selection. Conversely, to clear the selection, right-click in the box and select the Clear Selection.
- If a direction is selected, both Default Selection and Clear Selection items are available from the context menu.
- If a plane or a surface is selected as a Reference element then Reference direction field will be disabled, as reference location is computed as an intersection of that plane or surface with base surface. In this case OK and Preview buttons will be enabled.
Important: The intersection or projection curve must be long enough to join the base surface boundaries. The mating flange reference location feature is created in hidden mode and is temporarily shown during edition.
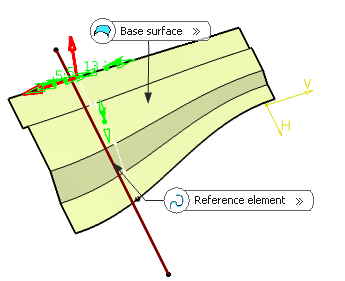
- Define the mating flange parameters by clicking the value
to edit in the dialog box or by clicking the handles in the 3D
geometry.
- Width
- Margin
- Wrap

-
Click Preview.

-
Define the thickness.
-
Default thickness: is generally the 3D shape thickness and is used as the default offset value. You can define its value either by entering a value in the box or using the handles in the 3D geometry.
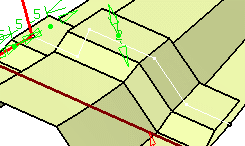
-
Local thickness: enables you to define multiple thickness values. They replace the default value and can be positive, negative, or null. Select a sub-part of the reference curve and define its value either by entering a value in the box or using the handles in the 3D geometry. This thickness value applies to all surfaces on which the curve lies as well as connected surfaces that are tangent continuous. You can select several sub-parts, each one having its own local thickness. For each value, a corresponding 3D dimension is created in the 3D geometry and can be edited by double-clicking it.
In case no local value is defined, the Local thickness box is unavailable. Otherwise, the corresponding sub-part and the 3D dimension are highlighted in the 3D geometry. If you select the highlighted sub-part, the local value is deleted and the default thickness value is used.
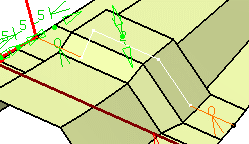
Note:- The thickness that is aggregated under the mating flange feature is the default thickness.
- You can create a mating flange on a portion of the base surface that contains a hole simply by setting the Default thickness to 0mm:
-
- Click OK
to create the mating flange.Its reference location is aggregated under the Mating Flange feature and can be used as an input for a further operation.