About Geometry Quality Enhancement | ||
| ||
Although imported content is respected as much as possible, poor geometry quality of the input data, or different tolerance and continuity constraints (e.g. imported data are seen as duplicated, not joined, or not continuous) will require that you improve the quality of the imported data. This is also required in case of unexpected result, or total or partial import failure (the elements are not imported, or are cut into several elements to respect the continuity).
- The standard checks, continuity optimization of BSpline curves and surfaces, and automatic healing are always performed.
- Healing operations are performed on faces, shells and solids, not on independent wires, points, ...
- Simplification is performed only on non closed faces, not on split closed faces.
- Automatic continuity optimization is performed only on BSpline curves and P-curves.
Two modes are available:
- The standard mode that does not allow a deformation.
- The advanced mode that allows a deformation that you can control. With Allow deformation, the support surfaces of the impacted faces may be fully modified, and new surfaces may replace the previous split surfaces.
In standard mode, Allow deformation is not selected, a standard optimization is performed:
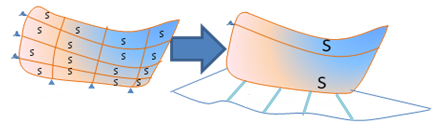
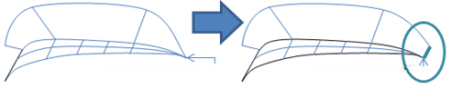
- BSpline curves and surfaces are optimized to reduce
the number of output elements. In the example below, the number of cuts is
reduced and the resulting surface has a continuous curvature.

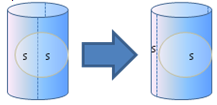
- Final surfaces are simplified (the seam can be
moved), if those surfaces are canonical, closed but supporting an open surface.
- Singularities are removed on curves and surfaces.
In the example below, a null curvature radius is changed into a non null one.

- In this mode, the maximum shape deformation is smaller than the tolerance (0.001 mm in normal range, 0.1 mm in large range), thus considered as "no deformation". If required, you can perform more enhancements by allowing a deformation.
In advanced mode, Allow deformation is selected.
When Allow deformation is selected, the standard steps described above are performed. Then:
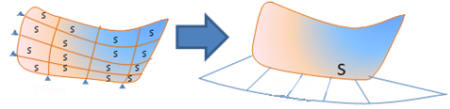
- When the resulting surface is still split, a new
simplified surface is created, resulting in a smooth curvature:
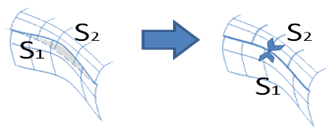
- For defective shells and faces, a G0 healing is
performed in addition to the topological and boolean healings. This can lead to
a deformation of the shape.
- Shape deformation is allowed when removing
singularities on curves and surfaces.
- Maximum shape deformation is the maximum allowed deformation defined by the resolution, multiplied by a factor (between 5 and 100) that you define with the slider.
After those healing steps are performed, the quality and compliance of all the imported faces, shells and solids are checked again. If defects still exist, they are reported in the error and report files.