Creating a Revision from an Existing Object | ||||||
|
| |||||
Context: The following diagram shows examples of
revisions created from existing objects: 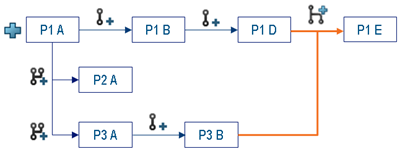
A new revision of P1 D (selected revision) is created in the P1 branch, using the content of P3 B. Therefore, P1 and P3 branches are merged.