Problem description
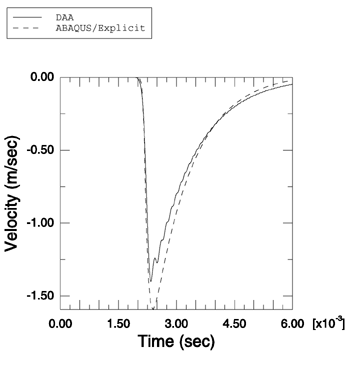
This problem models the interaction between two fluid-coupled elastic plates and a weak planar exponentially decaying shock wave with a maximum pressure of 1.57 MPa and a decay time of 1.0 ms. The second plate (the plate further from the shock source) is air-backed. In contrast to the solution from Schechter and Bort, engineering material parameters for the fluid and solid media are used. Both plates have a square cross-section of side 1 m and a thickness of 0.016 m. The separation between the plates is 3.2 m. The plates are made of steel with a density of 7850 kg/m3, a Young's modulus of 210.0 GPa, and a Poisson's ratio of 0.3. The fluid is water with a density of 1026 kg/m3, in which the speed of sound is 1528 m/s. Each plate is modeled with a single S4R element. A single stack of AC3D8R elements is used to model the fluid in front of the first plate and in between the plates. A planar nonreflective boundary condition is imposed at the end of the outer fluid column using surface impedance. The fluid response is coupled to that of the structure using a tie constraint on the relevant surfaces, with the plate surfaces as main surfaces. The fluid-solid system is excited by a planar exponentially decaying wave applied to the first plate using incident wave loading. A linear bulk viscosity parameter of 0.02 and a quadratic bulk viscosity parameter of 0.5 are used.