Problem description
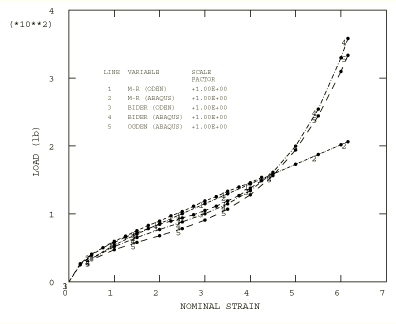
The geometry and the mesh for a quarter-sheet are shown in Figure 1. The undeformed square sheet is 2 mm (0.079 in) thick and is 165 mm (6.5 in) on each side. It has a centrally located internal hole of radius 6.35 mm (0.25 in). The body is modeled with 32 second-order plane stress reduced-integration elements (element type CPS8R). The incompressibility of the material requires the use of the “hybrid” elements for plane strain, axisymmetric, or three-dimensional cases; but in plane stress the thickness change is available as a free variable that can be used to enforce the constraint of constant volume (incompressibility), so this standard displacement formulation element (CPS8R) is appropriate. No mesh convergence studies have been performed, but the good agreement with the results given by Oden (1972) suggests that the model chosen has comparable accuracy with the model used by Oden.
Four different material models are used. The experimental data of Treloar (1944) composed of uniaxial, biaxial, and planar tension data are applied to these models. Two of the four models are forms of the standard polynomial hyperelasticity model in Abaqus. One is the classical Mooney-Rivlin strain energy function:
The other is due to Biderman:
In both cases the material is assumed to be incompressible. The constants used by Oden (1972) are = 0.1863 MPa (27.02 psi); = 0.00979 MPa (1.42 psi); and, for the Biderman model, = −0.00186 MPa (−0.27 psi), and = 0.0000451 MPa (0.00654 psi), with all other = 0. For the Mooney-Rivlin material is specified in the hyperelastic material definition (Hyperelastic Behavior of Rubberlike Materials), and only and are given. For the Biderman material and nine constants must be given. Since the material is incompressible the constants are set to zero.
The third material model is the Ogden hyperelasticity model in Abaqus:
The Ogden hyperelastic parameters are obtained using test data in the hyperelastic material definition to fit the experimental data of Treloar. Three pairs of parameters and are derived for .
The fourth material model is the Marlow hyperelasticity model in Abaqus. In this model the deviatoric part of the response is derived from one set of test data (uniaxial, biaxial, or planar) such that the material's behavior is represented exactly in the deformation mode for which test data are available. Three examples are provided in which the model is based on uniaxial, biaxial, or planar test data, respectively.
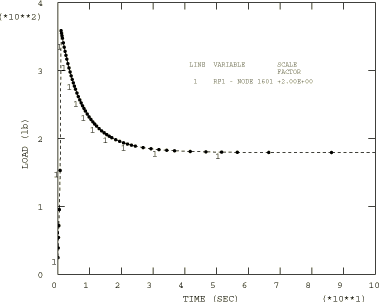
In addition, the Biderman model and the Marlow model are used in conjunction with the viscoelastic material model. The shear relaxation is defined by time-dependent moduli expanded in a Prony series with two terms:
with = 0.25, = 5.0 sec and = 0.25, = 10 sec. The bulk behavior is assumed to remain incompressible.