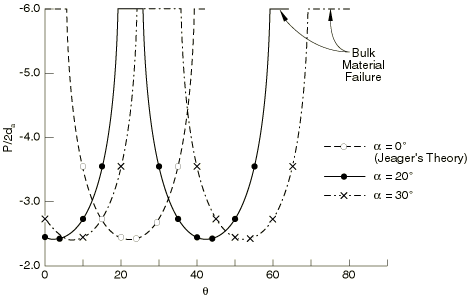
Problem description
We consider a sample of material subjected to uniaxial compression/tension. The material has two sets of planes of weakness having an included angle of 2. We seek to construct the failure envelope of the material as the orientation ( in Figure 1) of the planes of weakness is varied.
In the Abaqus model the failure surface for sliding on the joint systems is defined as
where is the pressure stress across the joint, is the shear stress magnitude in the joint, is the friction angle of the joint, and is its cohesion. For this problem we assume that for both joints 1000 (the units are not important), 45°, and that plastic flow in the joints is associated.
The behavior of the bulk material is based on the Drucker-Prager failure criterion
where is the Mises equivalent deviatoric stress (here is the deviatoric stress ), is the equivalent pressure stress, is the friction angle of the bulk material, and is the cohesion of the bulk material. For this problem we assume that 8000, 45°, and that plastic flow of the bulk material is associated.
When all the joints are closed, the material is assumed to be isotropic and linear elastic with a Young's modulus of 3 × 105 and a Poisson's ratio of 0.3. When a joint opens, the material is assumed to have no elastic stiffness with respect to direct strain across the joint system or with respect to shearing associated with this direction. Open joints, thus, create anisotropic elastic response.
Each test performed in this example is carried out using a cube (one C3D8 element) of unit dimensions. Displacements are prescribed at the nodes of the cube to simulate homogeneous deformation and stress conditions.