Problem description
The pipes have an outer diameter of 168.275 mm (6.625 in), with a 10.97 mm (0.432 in) wall thickness and a span of 1270 mm (50 in) between supports. The impacted pipe is assumed to be fully restrained at both ends, while the impacting pipe is allowed to rotate about a fixed pivot with an initial angular velocity of 75 radian/sec. We make use of symmetry boundary conditions to reduce the problem size by discretizing only the geometry to one side of the central symmetry plane.
Both pipes are made of steel with a Young's modulus of 207 GPa (30 × 106 psi), a Poisson's ratio of 0.3, and a density of 7827 kg/m3 (7.324 × 10−4 lb sec2in−4). A von Mises elastic, perfectly plastic material model is used, with a yield stress of 310 MPa (45 × 103 psi).
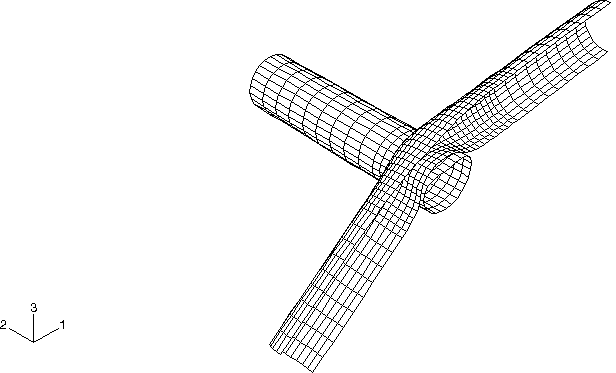
S4R shell elements are used to discretize the pipes. A higher level of mesh refinement is used near the middle of the pipes, where the impact will take place. The mesh is shown in Figure 1. The contact surfaces are defined over the entire length of each pipe and then grouped into a single contact pair. Kinematic contact enforcement is used for the primary input file, although models that use penalty contact pairs and general contact are also provided. An additional analysis with enhanced hourglass control is performed.