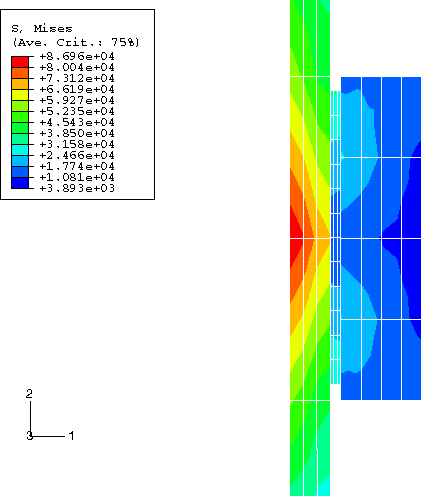
All parts of the model are elastic. The Young's modulus, Poisson's ratio, and density for the rod and the cylinder are 207 GPa (30.0 × 106 psi), 0.3, and 7800 kg/m3 (0.73 × 10−3 lbf s2/ in4), respectively. The compound has a Young's modulus of 6.9 GPa (1.0 × 106 psi), a Poisson's ratio of 0.2, and a density of 1069 kg/m3 (0.1 × 10−3 lbf s2/ in4).
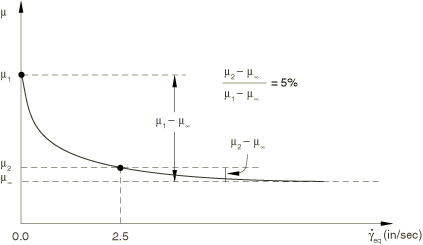
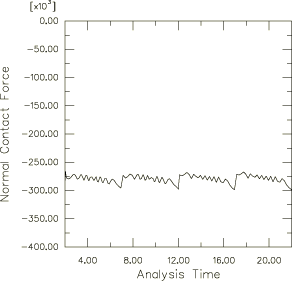
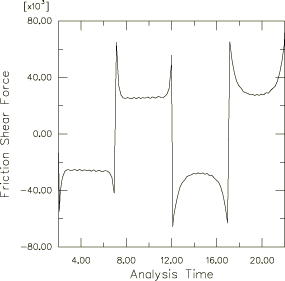
It is assumed that the interface between the slider and the compound is rough; i.e., no slip can occur when contact is established. The rough surface interface is modeled with the Lagrange friction model and a high friction coefficient. It is assumed that the interface between the rod and the compound is polished and has a static friction coefficient . Experimental tests show that the dynamic friction coefficient, , is 0.1 for a slip rate equal to 2.5 inches per second. Furthermore, the static coefficient decays exponentially to the kinetic friction coefficient, , according to , where is the decay coefficient. The dynamic coefficient at higher slip rates is not known; hence, the default Abaqus assumption that the ratio to is 5% is used. The idealized friction model is illustrated in Figure 3 and is specified using test data to fit the exponential model for frictional behavior. Abaqus calculates the kinetic friction coefficient and the decay parameter. For the cases that use the Coulomb friction model, the data for the friction coefficient and the corresponding slip rate have been provided in tabular form.