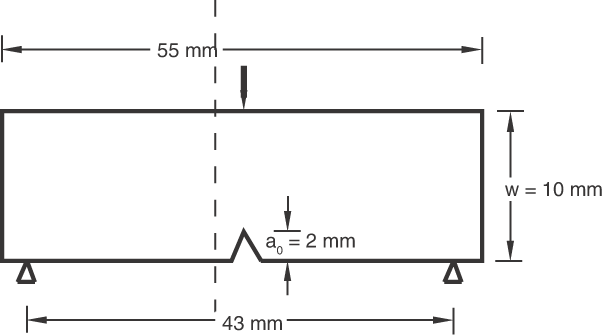
The loading of the specimen and the specification of the COD criterion for crack growth demonstrates the flexibility of the critical crack opening displacement criterion. Frequently, the crack opening displacement is measured at the mouth of the crack tip: this is called the crack mouth opening displacement (CMOD). The crack opening displacement can also be measured at the position where the initial crack tip was located. Alternatively, the crack-tip opening angle (CTOA), defined as the angle between the two surfaces at the tip of the crack, is measured. The crack-tip opening angle can be easily reinterpreted as the crack opening at a distance behind the crack tip. In this example the COD specification required to use both the CMOD and the CTOA criteria is demonstrated.
For the purposes of demonstration the crack opening displacement at the mouth of the crack is
used as the initial debond criterion. The first three nodes along the crack
propagation surface are allowed to debond when the crack opening displacement at
the mouth of the crack reaches a critical value. To achieve this, the following
loading sequence is adopted: in Step 1, the specimen is loaded to a particular
value (crack propagation analysis is not used), and in Step 2 the first
crack-tip node is allowed to debond (crack propagation analysis is used). Steps
3 and 4 and Steps 5 and 6 follow the same sequence as Steps 1 and 2 so that the
two successive nodes can debond. Since, the crack opening displacement is
measured at the mouth of the crack, the value of the distance behind the crack
tip along the secondary surface is different in Steps 2, 4, and 6.
The loading sequence adopted above outlines a way in which the CMOD measurements can be simulated without encountering the situation in which the COD is measured beyond the bound of the specimen, which would lead to an error message. In this example, the loads at which the crack-tip nodes debonded were known a priori. In general, such information may not be available, and the restart capabilities in Abaqus can be used to determine the load at which the fracture criterion is satisfied.
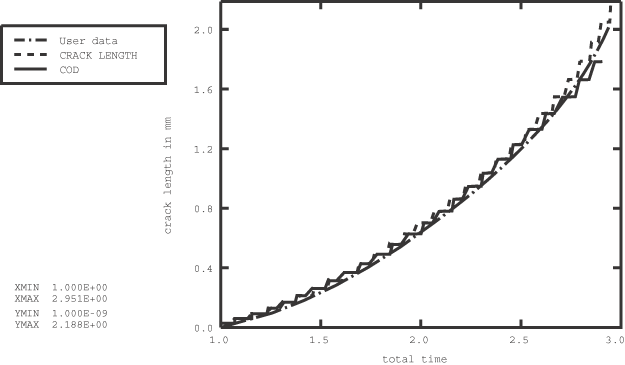
The remaining bonded nodes along the crack propagation surface are allowed to debond based on averaged values of the crack-tip opening angles for different accumulated crack lengths. The data prescribed under the crack propagation criteria in Step 7 are the crack opening displacement values that were computed from the crack-tip opening angles observed in the analysis that uses the prescribed crack length versus time criterion. These crack-tip opening angles are converted to critical crack opening displacements at a fixed distance of 0.04 mm behind the crack tip. Hence, the crack opening displacement is measured very close to the current crack tip.