Application description
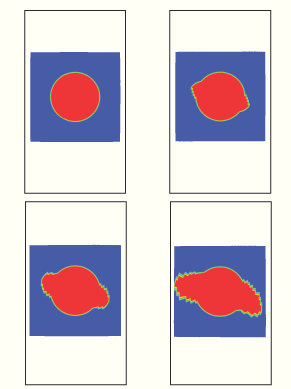
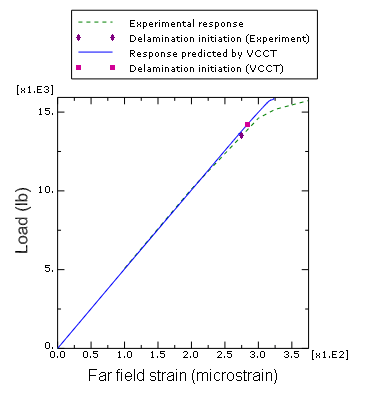
Delaminations are a primary failure mode for laminated composite materials. The delamination growth is more prominent under compressive loading since it results in buckling of a sublaminate leading to the delamination growth. The particular problem considered here is described in Reeder (2002). The results from the VCCT debond approach in Abaqus are compared to the experimental results.
Geometry
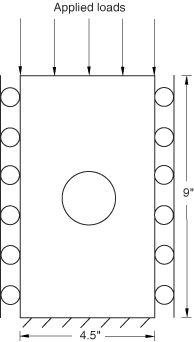
A flat 9.0 in (228.6 mm) × 4.5 in (114.3 mm) composite panel with a centrally located 2.5 in (63.5 mm) diameter delamination is studied in this example, as shown in Figure 1.
Materials
The panel is made of a AS4/3501-6 graphite/epoxy composite material system for which the typical lamina properties are given in Table 1. The laminate stacking sequence for the panel is [(±45/90/0)2/±60/±15]S. The critical fracture toughness for Modes I, II, and III at the delamination interface are also given in Table 1.
Boundary conditions and loading
The panel is subjected to compressive loading along its long axis. The overall dimensions of the model with boundary conditions and loading can be seen in Figure 1.