Assigning a Surface Interaction Definition to a Contact Pair
A surface interaction definition specifies the constitutive contact properties and the constraint enforcement methods used by a contact pair. Every contact pair in a model must refer to a surface interaction definition, even if the contact pair uses the default contact property models. See About Mechanical Contact Properties for information on defining contact properties. A non-default constraint enforcement method can be specified as part of a surface interaction definition, as described in Contact Constraint Enforcement Methods in Abaqus/Standard.
Multiple contact pairs can refer to the same surface interaction definition.
The surface interaction definition is also used to provide a non-default value for the surface out-of-plane thickness in the following cases:
a two-dimensional model, or
a contact pair involving a node-based surface to provide a non-default cross-sectional area at every node in the node-based surface.
Abaqus/Standard uses the out-of-plane surface thickness and cross-sectional area provided in the surface interaction definition to compute the contact stresses.
Input File Usage
Use both of the following options:
CONTACT PAIR, INTERACTION=interaction_property_name SURFACE INTERACTION, NAME=interaction_property_name
Example
Figure 1 shows the mesh used in this example. For purposes of this example, the surface
ASURF is the secondary surface of the contact pair. The
property definition for the contact pair (GRATING) uses
the finite-sliding, node-to-surface formulation with a friction model with
=0.4 and uses the default “hard” contact model for the behavior normal to
the surfaces.
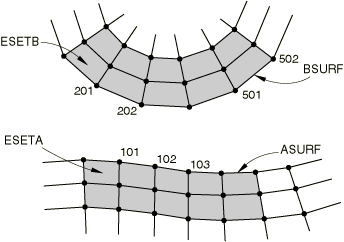
HEADING … SURFACE, NAME=ASURF ESETA, SURFACE, NAME=BSURF ESETB, CONTACT PAIR, INTERACTION=GRATING ASURF, BSURF SURFACE INTERACTION, NAME=GRATING FRICTION 0.4 NSET, NSET=SNODES 101, 102, 103 STEP, NLGEOM … END STEP