Damage initiation and damage evolution (Hashin criteria)
Elements tested
CPS3
CPS4
CPS4I
CPS4R
CPS6
CPS6M
CPS8
CPS8R
M3D3
M3D4
M3D4R
M3D6
M3D8
M3D8R
M3D9
M3D9R
S3
S3R
S3RS
S4
S4R
S4R5
S4RS
S4RSW
S8R
S8R5
S9R5
SC6R
SC8R
STRI3
STRI65
Features tested
The Hashin damage initiation criteria and energy-based damage evolution law are tested with a linearly elastic material.
Problem description
This verification test consists of a set of one- and two-element models subjected to uniaxial tension or compression for various angles (off-axis angles) between the fiber direction and the direction in which the load is applied. The default maximum degradation (equal to 1.0) is used for first-order elements, and the value of the maximum degradation of 0.95 was specified for the second-order elements.
Results and discussion
The degradation of the material stiffness starts when the Hashin initiation criterion is reached for at least one of the failure modes. The damage variables, for the damage modes for which the initiation criteria are satisfied, evolve according to an energy-based evolution law with linear softening. Once the damage variable reaches the maximum degradation specified, no further damage takes place.
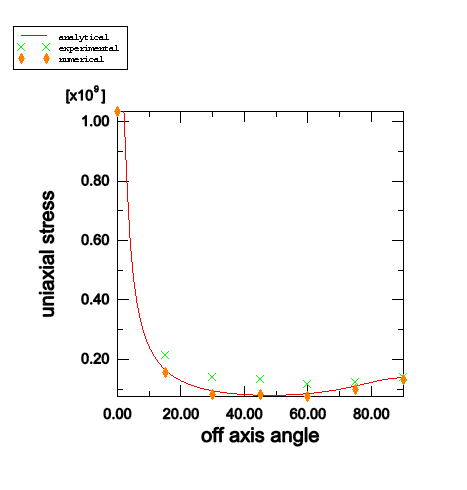
The results for the off-axis angles equal to 0° (fiber tension and compression) and 90° (matrix tension and compression) were verified to agree with analytical results.
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the unidirectional stress for tension and compression, respectively, at which the initiation criterion is satisfied as a function of the off-axis angle. In these figures the numerical predictions agree very well with the analytical results and also show good agreement with the experimental data reported in Jones (1999).

Input files
Abaqus/Standard input files
- damage_hsncomp_cps4r_0.inp
-
CPS4 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_cps4r_90.inp
-
CPS4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsncomp_cps6_90.inp
-
CPS6 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsncomp_cps6m_0.inp
-
CPS6M elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_cps8_0.inp
-
CPS8 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_cps8r_0.inp
-
CPS8R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_m3d8_0.inp
-
M3D8 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_m3d8r_0.inp
-
M3D8R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_m3d9_0.inp
-
M3D9 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_s4r_0.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_s4r_15.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 15°.
- damage_hsncomp_s4r_30.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 30°.
- damage_hsncomp_s4r_45.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- damage_hsncomp_s4r_60.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 60°.
- damage_hsncomp_s4r_75.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 75°.
- damage_hsncomp_s4r_90.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsncomp_s8r_0.inp
-
S8R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_s8r5_0.inp
-
S8R5 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_s9r5_0.inp
-
S9R5 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsncomp_sc6r_0.inp
-
SC6R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsnten_cps3_90.inp
-
CPS3 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsnten_cps4_30.inp
-
CPS4 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 30°.
- damage_hsnten_cps4i_60.inp
-
CPS4I elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 60°.
- damage_hsnten_cps4r_0.inp
-
CPS4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsnten_cps4r_90.inp
-
CPS4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsnten_m3d3_90.inp
-
M3D3 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsnten_m3d4r_0.inp
-
M3D4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsnten_m3d6_90.inp
-
M3D6 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsnten_m3d9r_0.inp
-
M3D9R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsnten_s3_0.inp
-
S3 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsnten_s3r_90.inp
-
S3R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsnten_s4_90.inp
-
S4 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsnten_s4r_0.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsnten_s4r_15.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 15°.
- damage_hsnten_s4r_30.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 30°.
- damage_hsnten_s4r_45.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- damage_hsnten_s4r_60.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 60°.
- damage_hsnten_s4r_75.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 75°.
- damage_hsnten_s4r_90.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsnten_s4r5_90.inp
-
S4R5 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 90°.
- damage_hsnten_sc8r_0.inp
-
SC8R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsnten_stri3_0.inp
-
STRI3 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 0°.
- damage_hsnten_stri65_90.inp
-
STRI65 elements subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 90°.
Abaqus/Explicit input files
- x_damage_hsnten_cps3_45.inp
-
CPS3 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_cps3_45.inp
-
CPS3 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_cps4r_45.inp
-
CPS4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_cps4r_45.inp
-
CPS4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_m3d3_45.inp
-
M3D3 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_m3d3_45.inp
-
M3D3 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_m3d4r_45.inp
-
M3D4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_m3d4r_45.inp
-
M3D4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_m3d4_45.inp
-
M3D4 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_m3d4_45.inp
-
M3D4 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_sc6r_45.inp
-
SC6R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_sc6r_45.inp
-
SC6R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_sc8r_45.inp
-
SC8R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_sc8r_45.inp
-
SC8R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_s3_45.inp
-
S3 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_s3_45.inp
-
S3 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_s3r_45.inp
-
S3R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_s3r_45.inp
-
S3R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_s4_45.inp
-
S4 elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_s4_45.inp
-
S4 elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_s4r_0.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 0°.
- x_damage_hsnten_s4r_15.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 15°.
- x_damage_hsnten_s4r_30.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 30°.
- x_damage_hsnten_s4r_45.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsnten_s4r_60.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 60°.
- x_damage_hsnten_s4r_75.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 75°.
- x_damage_hsnten_s4r_90.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial tension; off-axis angle, 90°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_s4r_0.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 0°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_s4r_15.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 15°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_s4r_30.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 30°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_s4r_45.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 45°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_s4r_60.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 60°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_s4r_75.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 75°.
- x_damage_hsncomp_s4r_90.inp
-
S4R elements are subjected to uniaxial compression; off-axis angle, 90°.
References
- “Mechanics of Composite Materials,” Taylor & Francis, Inc., pp. 102–112, 1999.