Actuation of connected rigid bodies
Elements tested
CONN3D2
Problem description
This verification problem tests the option of specifying connector motion to prescribe the relative motions of an articulated structure. A robotic-like crane assembly, modeled as rigid bodies connected together by means of connector elements, is subjected to actuating motions that drive the kinematic connections by specified amplitude curves. The actuating motions, including relative sliding and a two-axes rotation, cause the assembly to open up in a smooth sequence to form a riser crane. After a drilling and downward motion of the outermost body, the assembly closes down and reverts to its starting configuration. Tests are conducted both with no friction and with frictional effects in the connections.
Model:
The model consists of rigid bodies and connector elements as described in the table below. Each rigid body pair in the table is connected by rotational and translational basic connector types with connector motion definitions in each of the available relative components of motion.
| Body 1 | Body 2 | Basic Connector Types | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Translational | Rotational | ||
| Base | Arm 1 | SLOT | REVOLUTE |
| Arm 1 | Cover | JOIN | REVOLUTE |
| Arm 1 | Arm 2 | SLOT | ALIGN |
| Arm 2 | Riser 1 | CARTESIAN | CARDAN |
| Riser 1 | Riser 2 | SLOT | ALIGN |
| Riser 2 | Crane | JOIN | REVOLUTE |
| Crane | Chuck | JOIN | REVOLUTE |
| Chuck | Bit | CARTESIAN | CARDAN |
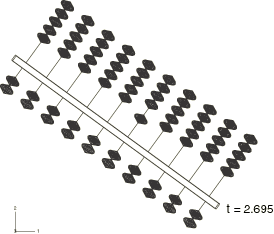
The complete model in the fully open configuration with the rigid bodies labeled is shown in Figure 1.

Results and discussion
Abaqus provides the expected solution for all cases.
Input files
- conn_std_craneactuation.inp
Abaqus/Standard input file.
- conn_std_craneactuation_fric.inp
Abaqus/Standard input file with friction.
- conn_xpl_craneactuation.inp
Abaqus/Explicit input file.
- conn_xpl_craneactuation_fric.inp
Abaqus/Explicit input file with friction.