Elements tested
PD3D
ProductsAbaqus/Explicit Elements testedPD3D Features tested
Problem descriptionThe probability density of generator particles and the mass flow rate per inlet area of generated particles are tested for four particle generators, each generating a single particle species. Each particle generator has a single faceted inlet surface with constant dimensions of 7 mm × 7 mm. Table 1 lists the particle size probability density function (PDF) type and parameters for each particle generator species. The mass flow rate per unit inlet area for each particle generator species is held constant for the duration of the analysis. Particles of all species have a constant entry speed of 1000 mm/s. All generated particles in this problem continue to travel with the entry velocity along the normal direction to the generating inlet facet. Each particle generator can generate a maximum of 20000 particles. Figure 1 presents a view that is normal to the inlet facets showing the generated particles at the end of the analysis. 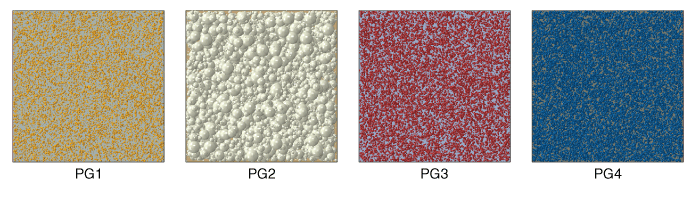
Results and discussionA direct user time increment of 1.0 × 10−4 s was specified for the analysis. Generated and specified PDFs and mass flow rates are compared for particle generators PG1, PG2, PG3, and PG4. Comparison of generated PDFThe specified normal and the log-normal probability density functions for particle generators PG1 and PG2, respectively, are truncated PDFs. Truncated analytical PDF curves are compared to the generated results for these two cases (see Probability Density Function for more details on truncated PDFs). Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the comparison of generated PDFs with the specified truncated PDF for generators PG1 and PG2, respectively. Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the comparison of generated uniform and piecewise linear PDFs with the corresponding specified PDFs for generators PG3 and PG4, respectively. The two main factors influencing the agreement between the generated and specified PDF are the rejection of candidate particle sizes during the generation process (see Particle Generator for further details) and the number of particles being generated. The figures show that the generated PDF follows the specified PDF in an average sense in all four cases. Comparison of generated mass flow rateSince the inlet area does not change, the mass flow rate (MFR) for this problem is Figure 6, Figure 8, and Figure 9 show the comparison of achieved to specified mass flow rates for particle generators PG1, PG3, and PG4, respectively. Particle generators PG1, PG3, and PG4 exhaust the maximum number (20000) of particles and halt generating particles, causing the mass flow rates for these generators to drop to zero at 0.004 s, 0.0085 s, and 0.0138 s, respectively. The achieved mass flow rate closely matched the specified mass flow rate for these three particle generators. Particle generator PG2 generates 8048 particles during the analysis. Figure 7 shows the comparison of achieved to specified mass flow rate for particle generator PG2. Due to the discrete nature of particle generation and larger particle sizes, the achieved mass flow rate matched the specified mass flow rate only in an average sense for particle generator PG2 (see Particle Generator for further details). Input files
Figures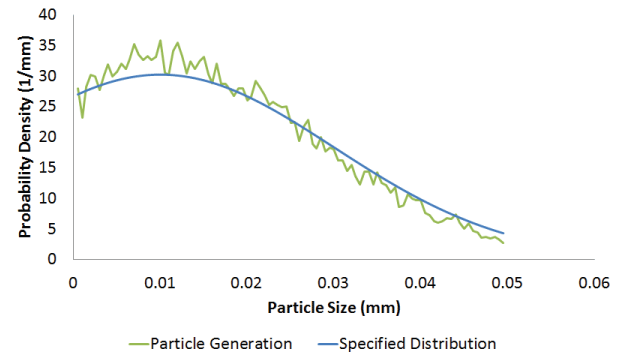 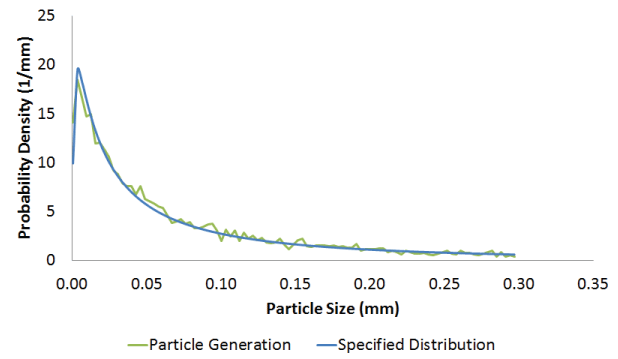  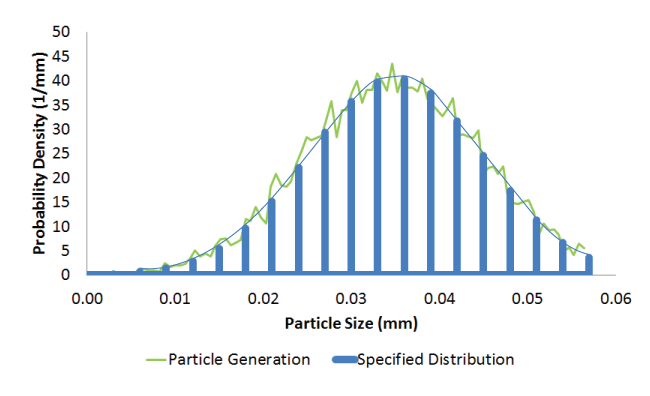 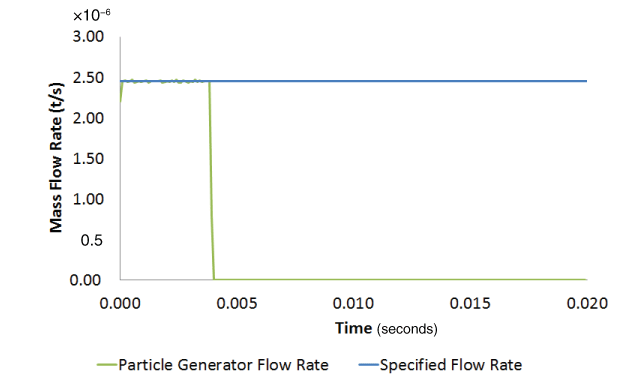 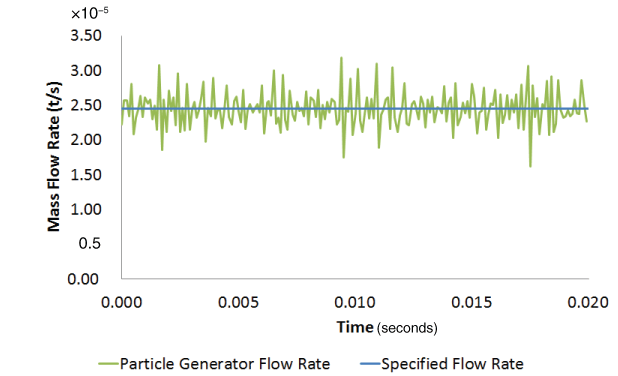  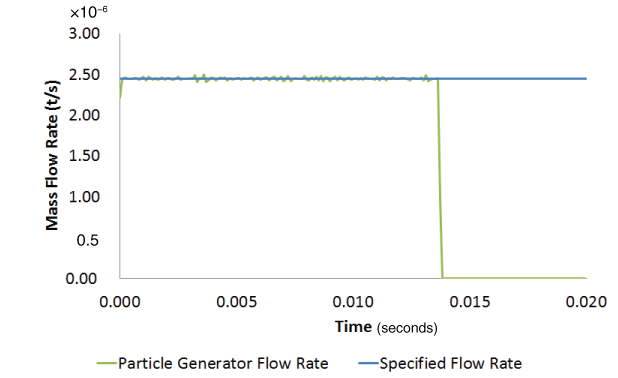 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||