Additive Manufacturing Scenario Creation
Additive Manufacturing Scenario Creation simulates two classes of additive manufacturing processes: powder bed and direct material deposition.
In a powder bed–type additive manufacturing process, like selective laser sintering (SLS) and stereolithography (SLA), a recoater or a roller blade deposits a single layer of raw material. Then, a high-powered laser scans a single cross-section of the part over the layer of raw material to fuse it with the previous layer underneath. The raw material deposition layering is simulated by progressive element activation in a structural or a thermal analysis. The laser-induced heating is simulated by a moving heat flux in a thermal analysis.
In direct material deposition, the raw material and heat source are applied at the same time and location. In a fusion deposition modeling (FDM)-type additive manufacturing process, the raw material is injected through a nozzle onto a platform. The nozzle traces the pattern for each layer with the raw material. Materials are typically deposited layer by layer until the build is complete. The raw material can be deposited in a molten state that hardens as it cools. In some processes, such as laser direct energy deposition (LDED), the raw material is injected in a powdered form and then heated in place by a laser beam.
Additive Manufacturing Scenario Creation also supports two different simulation workflows for additive manufacturing processes, thermomechanical and eigenstrain-based.
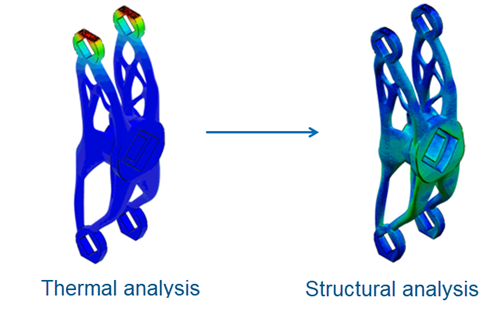
A thermomechanical simulation consists of a transient heat transfer analysis of thermal loads introduced on a part during the printing process. The thermal analysis is followed by a static structural analysis that is driven by the temperature field from the thermal analysis. The simulation allows exact specification in time and space of processing conditions and gives you precise control over the fidelity of the solution. The simulation is accurate and comprehensive, but it can be computationally expensive with increasing time and spatial (mesh) resolution.
Consider the aspects of the process in the thermal and stress simulations. For the heat transfer (thermal) analysis:
- Progressive material deposition: every additive manufacturing process adds new material with time, changing the thermal profile of the model.
- Progressive heating of the deposited material: for some additive manufacturing processes, the newly deposited layer of material is heated to the melting point, causing the material to fuse to an underlying layer or a substrate.
- Progressive cooling of the printing part: as a part is printed, its cooling surface is continuously evolving with time.
For the stress analysis:
- Temperatures from the heat transfer analysis drive the stress analysis.
- Progressive material deposition requires similar techniques as those used in the heat transfer analysis.
- Temperature-dependent material properties can be used to produce accurate stress results.
The eigenstrain-based processes uses eigenstrains, or inherent strains. Eigenstrain is an engineering concept used to account for all possible sources of permanent (or inelastic) deformation induced by the process. Eigenstrain has long been used for the evaluation of residual stresses from welding operations. An eigenstrain-based simulation of an additive manufacturing process consists of a single static stress analysis of a printing part. A predefined eigenstrain field is applied according to an element activation sequence representative of the process (usually layer by layer). This process results in a distribution of residual stresses and a deformation field that can lead to the overall distortion of the part. This method eliminates the need to obtain detailed machine information; however, it requires that you calibrate eigenstrain values from experiments or detailed process-level thermomechanical simulations. The results from an eigenstrain-based simulation are typically more approximate than a thermomechanical simulation. Generally, the eigenstrain analysis is sufficient to capture distortion and residual stresses. However, it might not capture higher-order deformation modes, such as the buckling that can happen in thin-walled components during printing.
Additive Manufacturing Scenario Creation can work independently or incorporate data from the Powder Bed Fabrication app. Using data from Powder Bed Fabrication helps tie the simulation to your additive manufacturing process. It also supports options such as the use of perforated supports. For simulation, perforated supports are modeled as solids with the mass, stiffness, and thermal conductivity automatically scaled down to account for the perforation data.
Additive Manufacturing Scenario Creation provides four different options for simulating an additive manufacturing process. Three of the options are for powder bed-type AM processes, and the fourth is for FDM- and LDED-type AM processes:
- Thermal-Mechanical For Powder Bed
- Eigenstrain For Powder Bed
- Pattern Based Thermal-Mechanical For Powder Bed
- Thermal-Mechanical For FDM/LDED