Paint Brush Model
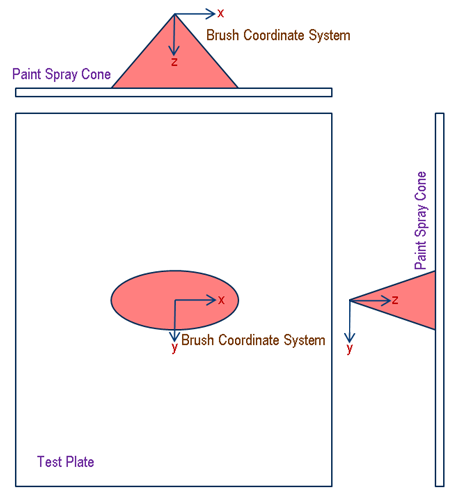
The paint brush that is to be used in the process is quantified in preparation for simulation based on a couple of simple user experiments that will determine the particular paint gun being used on the shop floor.
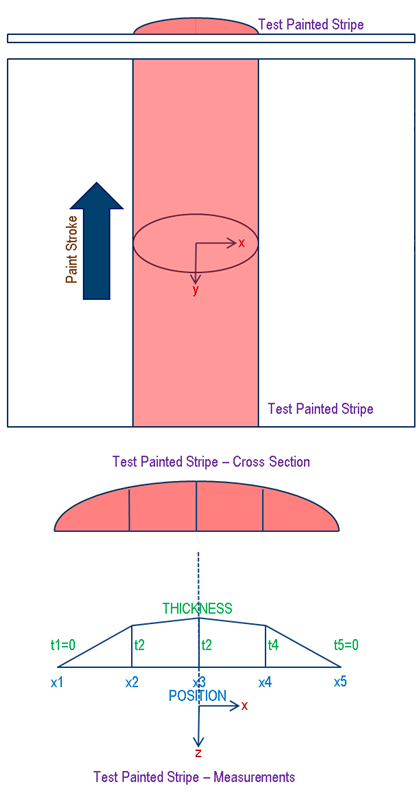
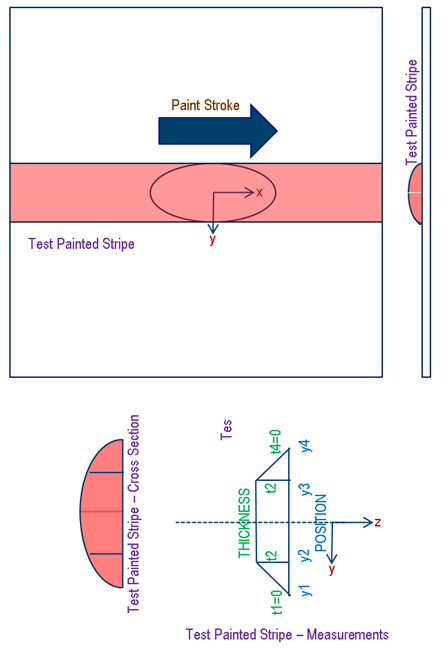
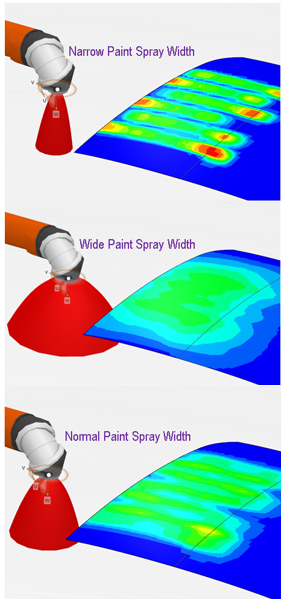
The experiment consists of painting a stripe on a test plate using the actual brush and measuring the thickness profile of the deposited paint once it has dried. The stripe is painted from a fixed target distance height above the plate and at a constant TCP speed for the robot used in the paint test experiment. The paint fluid flow rate through the AB or ERB paint gun, as well as the percentage solids content information for the paint used, are noted as part of the experiment. In addition to these two parameters, if the paint gun is of type ERB, additional note is made of the disk rotation speed, regulation air pressure, regulation air volume, and electrostatic voltage used during the experiment. You can also specify as part of their experiment a shaping factor for each of the above four parameters. The shaping factor determines the extent to which the parameters cause a change in the ERB paint spray width. In the case of the disk rotation speed parameter, a default value of 1.0 implies that doubling the disk speed will double the spray width. For each of the remaining parameters (regulation air pressure, volume and electrostatic voltage), a shaping factor of 1.0 implies that doubling the parameter will halve the spray width.
These test parameters, along with the measured paint deposition thickness profile, are entered into the Calibration tab of the paint profile for the robot being used in the painting tasks. The spray from an AB paint gun can be non-symmetrical and hence the experiment consists of painting two stripes, one in the X direction and one in the Y direction. The paint sprayed by an ERB paint gun is symmetrical and hence only one testing pass in the X direction is required. In the case of the AB paint gun, based on the two measured test profiles in the X and Y directions the paint spray is visualized as an elliptical cone. The paint spray for an ERB paint gun is visualized to be parabolic in the side view and circular in the top view. The actual paint deposition during simulation is then computed by extrapolating these paint and brush properties as modified by the settings in the current paint profile of the task and all other effects of robot motion, brush alignment and distance, painted part shape and surface curvature etc. The selection and consequence of the simulation paint profile settings are described further below.

The test is conducted with this type of a pair of X and Y passes so that the paint brush deposition behavior can be represented in the form of two orthonormal probability distributions that are then convoluted and extrapolated mathematically during simulation. Since one cannot do an actual paint deposition measurement experiment with a stationary paint gun, the robot is moved at a constant speed during the test that allows the paint volume flow rate to be related to the cross sectional area of the measured paint profile. Note that, due to conservation of paint volume, since the X and Y tests are conducted at the same speed, the areas under the X and Y profiles should be identical. Due to experimental error, the measured X and Y profile areas are likely to be slightly different and hence the system will automatically normalize the X and Y profiles at the time of user profile definition. Once the user has entered the calibration information, the system also calculates and displays the resulting effective computed gun transfer efficiency of the painting test. This efficiency represents the fraction of the sprayed paint (in terms of the paint solids) that is measured to have ended up being applied on the painted test surface after the experiment. The fraction of paint solids not applied to the surface is expected to have been lost to diffusion and overspray.