-
From the Sketch section of the action bar,
click
Equidistant
Points
 . .
-
Select an element.
Note:
You can select a line, a spline or two points you want to add
equidistant points between.
The Equidistant Point dialog box appears. By default, ten
equidistant new points are previewed.
To create the equidistant points in reverse direction, click
Reverse Direction
 . .
-
Select one of the extremity points of the line as the starting
point.
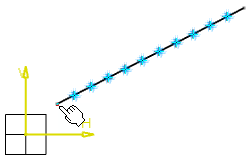
The
Parameters and
Spacing boxes are available. By default, the
New Points box is available.
-
In the
New Points box, enter the required number.
Notes:
- If you type a value in the box, you have to press
Enter to update the point distribution.
- If you use the arrows to modify the value, the point
distribution is automatically updated.
-
In the
Spacing box, enter the spacing between two
points.
Two points are displayed and distributed along the line.

-
In the
Parameters list, select
Points & Length.
-
In the
Length box, enter a value.
The length value represents the distance between the
starting point and the last new point created.
-
Press
Enter if needed.
The point distribution is modified.

-
In the
Parameters list, select
Spacing & Length.
-
In the
Spacing and
Length boxes, enter respective values.
-
Press
Enter if needed.
Three new points are now displayed, but the point
distribution is not modified.
Notes:
- When you create equidistant points on a curve where the curve
is used as a support, curvilinear distance constraints are created.
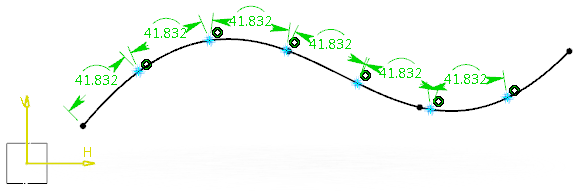
- When the sum of equivalent dimensions is greater than the
length of the support curve, the number of points are automatically adjusted.
Only the points whose sum of dimensions is less than the length of the curve
are created. For example, if the curve length is 100 units and you want to
create 15 points with equivalent dimensions of 10 units, only ten points with
equivalent dimensions are created.
-
Expand the
Relations node in the
tree
and double-click
EquivalentDimensions.x
.
The
Equivalent Dimensions Feature Window dialog box
appears displaying all the formulae for the equidistant points.
-
Optional: Enter the desired value for modifying the
distance parameter.
The value is changed for all the distance parameters.
Note:
If the curve is not fully constrained and you enter equivalent
dimensions whose sum is greater than the curve length, then the curve is
automatically adjusted.
|