Creating an Application (Methodology) | ||
| ||
|
Step |
Description |
See ... |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Define the Search-Based Application scope.
|
|
|
2 |
Create Connectors.
|
|
|
3 |
Create the Data Model. Create the metas and facets that you want to use in your application (see Indexing Options for Data Model Properties):
|
|
|
4 |
Configure the behavior of the search fields.
|
|
|
5 |
Prepare the content to display in search results (hits). (1) Number of hits to display in the page (2) Summary descriptions (3) Highlighting of terms (4) Browsable thumbnails (5) Hit metas (6) Hit facets 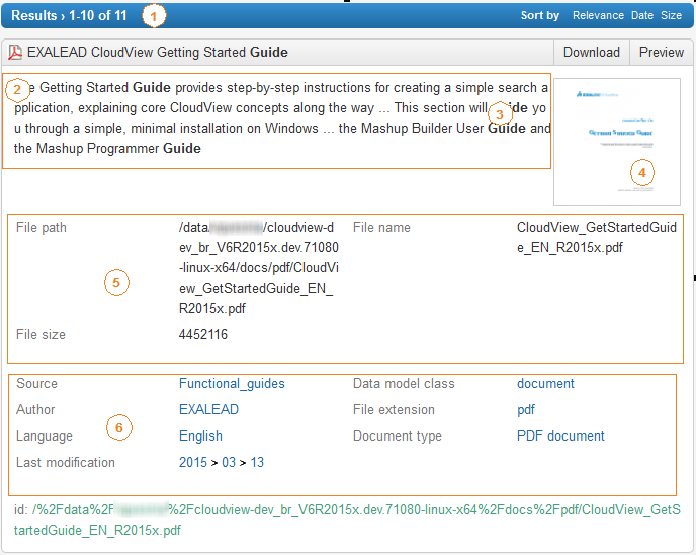 |
|
|
6 |
Define the refinement facets. They will be used to filter search results and navigate through them. By default, they display a count of documents but you can add other calculations. 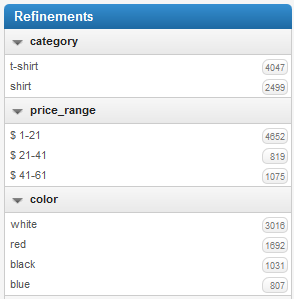 |
|
|
7 |
Create the front end of your application with the Mashup Builder.
Note:
You can also create use your own tools to communicate with the Exalead CloudView Search API. |
|
|
8 |
Optionally, secure the access to your documents. |