What's New | ||
| ||
R2022x FD01 (FP.2205)
- When you use a fluid material with density that varies with temperature, the incompressible fluid solver now automatically accounts for the varying temperature field in the simulation.
- You can now specify the pressure dissipation term and the pressure gradient formulation for a flow step, which lets you fine-tune the solver behavior for greater accuracy or greater likelihood of convergence.
- You can now run a multiphase simulation using the VOF Method that also includes compressible flow.
Temperature-Dependent Density Correction in the Incompressible Solver
Benefits: Incompressible flow simulations can produce more realistic results for
scenarios when the fluid density is not homogenous in space.
For more information, see
Density
Advanced Flow Solver Parameters for Improved Convergence
Benefits: The pressure dissipation term and pressure gradient formulation provide
greater control over the solver behavior, which allows you to fine-tune your simulation
for greater accuracy or greater convergence.
For more information, see
Defining Expert Numerics Controls
Support for Compressible Flow in Multiphase Simulations that Use the Volume of Fluid (VOF) Method
Benefits: With both compressible flow and multiple phases, you can simulate fluid flow
in which one of the two phases is compressible.
For more information, see
About the Volume of Fluid (VOF) Method
R2022x GA
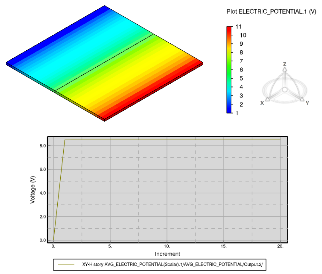
- You can now specify the electrical resistance between solid surfaces when the electric potential solver is active.
- You can now create history output requests to measure the area-averaged electric potential and the total average electric current across a solid component, such as a battery pack.
- You can override the operating parameters that you predefined for the new e-cooling components (that is, heat sinks, compact printed circuit boards, and thermoelectric coolers) now available in Fluid Model Creation.
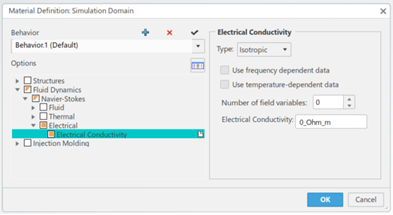
- You can now specify isotropic electrical conductivity in the material that you apply to solid components in a fluid flow simulation.
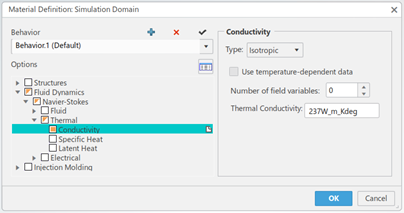
- You can now simulate orthotropic thermal conductivity for solid geometry that is defined using cylindrical geometry.
- This example guides you through performing an analysis of a shell-and-tube heat exchanger to determine its efficiency.
- You can include an additional pressure dissipation term that provides extra stability and robustness in simulations that include flow through porous media.
- You can now specify the momentum pressure gradient formulation for a step, which controls how the simulation calculates the pressure term in the momentum equation.
- You can now find the reference information you need to use the content delivered along with your app.
Electrical Resistance between Solid Surfaces
Benefits: The ability to specify the electrical resistance between solid surfaces
supports workflows that model the electrical current flowing through solid
components.
For more information, see
Defining a Solid Interface
Determining the Electrical Resistance of Solid Components
Benefits: The addition of area-averaged electric potential and total average electric
current history output requests allows you to determine the electrical resistance of
solid components.
For more information, see
CFD Output Variables
Support for New E-Cooling Components
Benefits: The ability to override an e-cooling component's operating parameters allows
you to reuse the component to run various simulations in Fluid Scenario Creation.
For more information, see
E-Cooling
Isotropic Electrical Conductivity for Solid Components
Benefits: Using materials that specify electrical conductivity lets you model common
workflows used in battery simulations.
For more information, see
Navier-Stokes: Electric Conductivity
Orthotropic Thermal Conductivity for Cylindrical Solid Geometry
Benefits: You can now specify more complex thermal behavior for geometry defined using a
cylindrical coordinate system.
For more information, see
Conductivity
New Simulation Example: Heat Exchanger Efficiency
Benefits: The heat exchange example provides step-by-step instructions that you can
perform to learn how to create a flow simulation with thermal effects.
For more information, see
Heat Exchanger Efficiency
Improved Robustness for Simulations that Include Porous Media
Benefits: Adding an additional pressure dissipation term can help your simulation
converge on a solution when it includes flow through porous media.
For more information, see
Defining Expert Numerics Controls
Improved Accuracy for Simulations with Incompressible Multiphase Flow, Multiple Reference Frames (MRF) Zones, or Body Forces
Benefits: The momentum pressure gradient formulation provides extra control for
improving the accuracy of the calculations when incompressible multiphase flow, multiple
reference frames (MRF) zones, or body forces are present in the simulation.
For more information, see
Defining Expert Numerics Controls
3DEXPERIENCE Native Apps Content Reference Guide
Benefits: The new guide provides one central location for all user assistance on the
content provided with 3DEXPERIENCE roles.
For more information, see
3DEXPERIENCE Native Apps Content