What's New | ||
| ||
R2022x FD01 (FP.2205)
- You can now associate several reference tables with an FMEA table.
- When opening the FMEA app, a new home page appears.
- Computed formulas can now be evaluated on demand and stored.
- You can now directly edit and export attributes on occurrences in tables depending on the used template.
- You can now customize the labels displayed in the trees and in the FMEA tables. The configuration of the patterns that define the labels of the PLM objects is done using Collaborative Spaces Control Center.
- You can now configure a URL for external modules provided by partners. The definition of URLs is done using Collaborative Spaces Control Center.
- You can now hide the calculated propagation effects for a more synthetic view.
- You can now define a fault isolation manual, which represents the association of fault isolation procedures to symptoms.
- The fallible references can now be organized in bookmarks in the Fallible Reference Editor.
- In the Structure Tree, if a function requirement or an operation requirement exists in a causality relationship, you can visualize induced elements such as failure modes, controls, or issues as children.
- You can access the User Assistance panel by hovering over a command tooltip from the action bar and clicking More help, if these elements exist.
Associating Reference Tables
Benefits: An FMEA table can now
reference several reference tables, which contain information.
For more information, see
Associating Reference FMEAs with an FMEA
Home Page
Benefits: The home page provides a quick access to start activities and to load recent elements.
For more information, see
Standard Area
Improving Support of Computed Attributes
Benefits: Computed attributes can now be persistent, searchable (for example using the
6WTags
panel), exported to XML, and displayed in other apps.
For more information, see
Refreshing Computed Attributes
Managing Attributes on Occurrences
Benefits: You can now analyze each equipment, which can have different attributes in
context.
For more information, see
Attributes on Occurrences
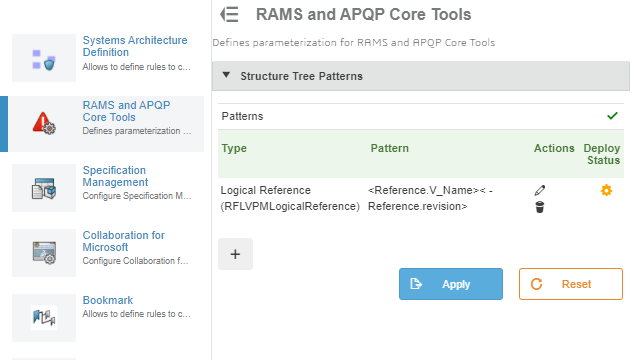
Customizing Labels in Trees and Tables
Benefits: Object labels can now follow the naming of your company.
For more information, see
Labels Configuration
Configuring Partner URL for External Modules
Benefits: External partner modules can now be called by the templates.
For more information, see
Modules
Hiding Computed Effects and Identifying Failure Propagation Loops
Benefits: You can now easily visualize propagation loops to fix them.
For more information, see
Displaying Computed Effects
Displaying a Propagation Tree
Linking Fault Isolation Procedures to Symptoms
Benefits: From a testability point of view, you can now isolate ambiguous symptoms using
fault isolation procedures and fault isolation manuals.
For more information, see
Linking Fault Isolation Procedures and Symptoms
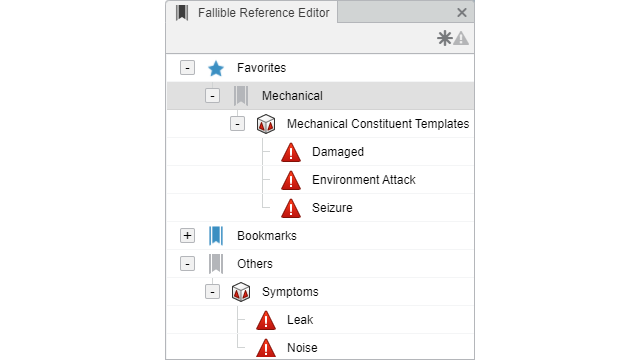
Improving Integration to Bookmarks
Benefits: The Fallible Reference Editor is now initialized with the
fallible references that are used in the currently loaded FMEAs.
For more information, see
About the Fallible Reference Editor
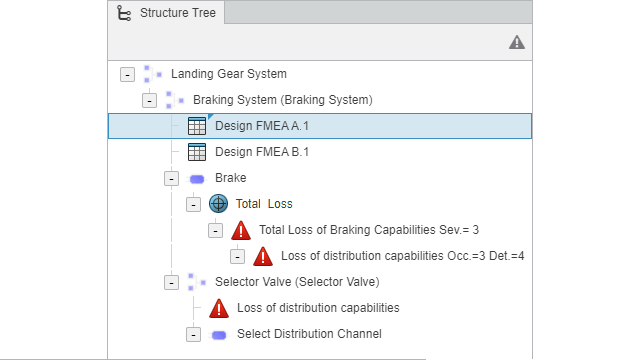
Improving Content of Structure Tree
Benefits: You can easily visualize the elements of the FMEA table
in the Structure Tree.
For more information, see
About the Structure Tree
User Assistance Provided within Failure Modes & Effects Analysis
Benefits: The information provided in the User Assistance panel helps you to learn short
information about some commands directly without opening the User Assistance
Portal.
R2022x GA
- If some cells of the table can contain multiple values, you can assign group numbers to the object contained in the cells.
Managing Groups in Multivalued Cells
Benefits: Objects in the cells of your tables can now be sorted in ascending order based
on group numbers.
For more information, see
Managing Logical Groups