How to Proceed
Below are listed the recommended steps.
- Before proceeding, read About the Tessellation Segmentation Scope.
- The general operation mode is explained in Recognizing Areas by Tessellation Segmentation.
- Analysis and healing of the tessellation.
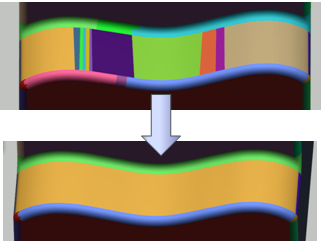
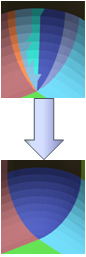
- Automatic segmentation of the tessellation:
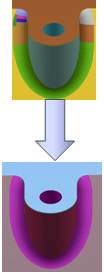
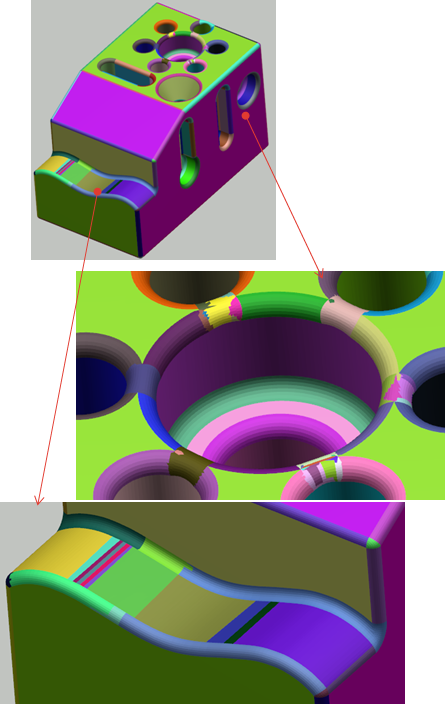
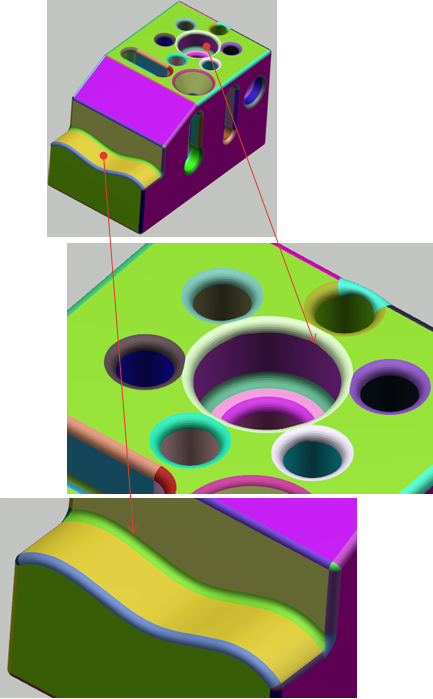
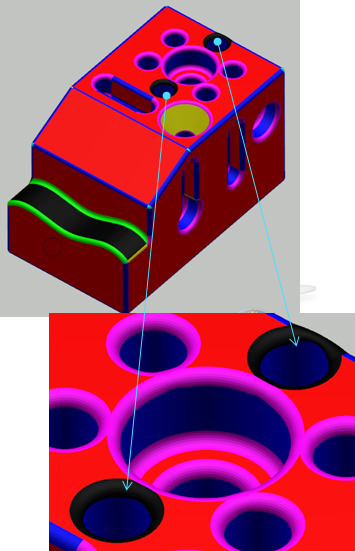
- Computation of a first BRep. See Analysis and Edition of the BRep.
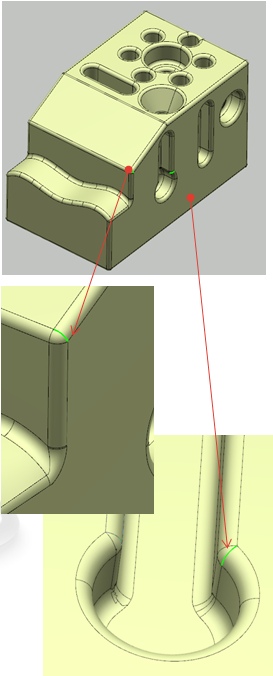
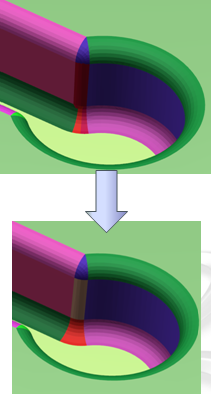
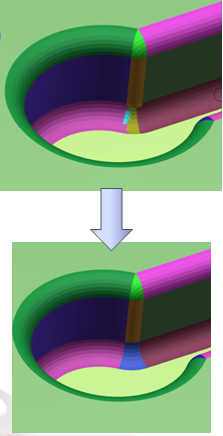
- Visualization of the BRep faults and free edges. See Analysis and Edition of the BRep.
- Edition of the segmentation around the faults. See Analysis and Edition of the BRep.
- Edition of areas
- Edition of types.
- Computation of a second BRep (repeat visualization of the BRep faults and free edges, if need be).
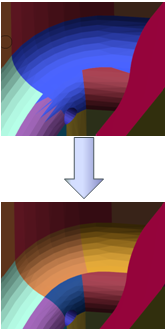
- Surfacic correction of the BRep with:
- Healing
- Close Surface.