What's New | ||
| ||
R2022x FD01 (FP.2205)
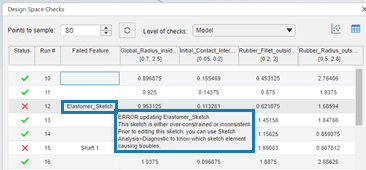
- You can now center the tree on failed design points, get more details about failed points, and disable model view updates while you check design points.
- The credit or token use for design improvement studies that change only the geometry is updated.
- You can now include plastic strain magnitude as a response variable for optimizations.
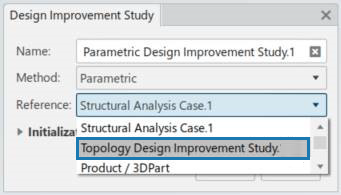
- You can now use completed shape or topology studies as the reference for new parametric design improvement studies.
- You can now check the mesh uniformity for a body in a design space to confirm that the size distribution for its elements is ideal for a topology optimization study.
- You can now perform studies for models meshed with any solid element types.
- When you submit a shape optimization study for analysis using the unified licensing model, the app now reduces the number of credits or tokens required to run the design cycles as the study progresses.
Enhancements to Design Space Checks
Benefits: You can focus review details about the cause of failed design points to decide
whether to explore similar designs. Disabling the updates to the model view saves the
computational resources normally used to render the model for each design point.
For more information, see
About Design Space Checks
License Reduction for Geometry Studies
Benefits: You now need fewer licenses to complete geometry-only studies, reducing the
overall cost.
For more information, see
License Reduction for Design Improvement Studies
Plastic Strain Response Variables, Objectives, and Constraints
Benefits: Including plastic strain magnitudes in your optimization increases the ability
of your design to measure the plastic strains in the design and control them as part of
the optimization process.
For more information, see
About Plastic Strain Magnitude Response Variables
Combining Parametric and Nonparametric Studies
Benefits: You can combine parametric and nonparametric studies to analyze your products
and improve your designs.
For more information, see
About Design Improvement Studies
Mesh Uniformity Checks for Topology Optimization Design Improvement Studies
Benefits: When you create a fine, uniform mesh before running the topology optimization,
you can produce a better optimized shape.
For more information, see
Creating a Design Space
Expanded Support for Solid Elements
Benefits: Design improvement studies now support the same full range of mesh types for
solid models as regular analysis cases. This expands the capability to reference an
existing analysis case for a study without changing the mesh.
For more information, see
About Design Spaces
License Attenuation for Shape Optimization Studies
Benefits: Shape optimization studies require fewer credits or tokens, reducing the
overall cost.
For more information, see
Running a Simulation