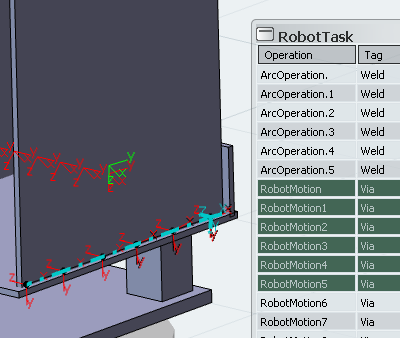
The orientation Robot snaps to the tag for the selected operation.
In addition to selecting operations in the table, you can also select individual tags and entire trajectories directly in the work area. As shown below, a line that represents a trajectory appears when you hover over it. The resulting selection highlights all operations that belong to the selected trajectory in the Results dialog box.
A context toolbar also appears that provides the Flip positioner  and Flip tool
and Flip tool  commands.
commands.
Flip tool provides for variations of TCP z-axis orientation. Occasionally the orientation of a tag can cause an undesirable initial robot posture:
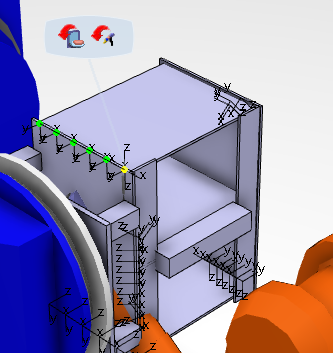
This posture can be corrected by selecting Flip tool  in the context toolbar:
in the context toolbar:
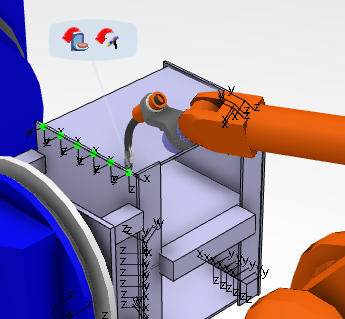
- Flip tool is performed only on the operations selected in the Results table.
- Flip tool is performed only on currently active joint(s). Active joints can be seen in the Joints column.
- You can continue to adjust the tool orientation by activating Reach and using the orientation Robot to adjust the roll angle.
When activated, Flip tool recalculates each of the Reach disc zones.
Flip positioner  allows you to to maintain a desired tool orientation (Flat, Horizontal, Vertical). At the same time, positioner joint values are different and allow for better robot access, fixture collision avoidance, etc.
allows you to to maintain a desired tool orientation (Flat, Horizontal, Vertical). At the same time, positioner joint values are different and allow for better robot access, fixture collision avoidance, etc.
The following image shows a trajectory that has six points, with three being unreachable and three that are classified as reachable yet out of limits (joint limits).

Using Flip Positioner, you can make all elements of the trajectory reachable.
