Introduction | ||
| ||
Problem Description
This example models the heat generated by a CPU chip attached to a heat sink on a printed circuit board. The board is enclosed by a case and cooled by a fan. The case is 200 mm x 100 mm x 40 mm and is modeled as a thin surface. The fan blows air into the case through an inlet, and the air exits the case from five small vents on each side of the enclosure.
The air is assumed to have a thermal conductivity of 0.025 W/mK, a specific heat of 1005 J/Kkg, a density of 1.25 kg/m3, and a viscosity of 1.8e-5 Ns/m2. The aluminum heat sink consists of 21 uniformly spaced fins with an aspect ratio X/L (X = spacing between the fins, L = height of each fin) = 1/11. The aluminum has isotropic material properties—a thermal conductivity of 237 W/mK and a specific heat of 910 J/Kkg. The heat source is a 50-mm x 50-mm x 5-mm silicon CPU chip. The chip has isotropic material properties—a thermal conductivity of 149 W/mK and a specific heat of 710 J/Kkg.

![]() Inlet
Inlet
![]() Outlets
Outlets
![]() Chip
Chip
![]() Heat Sink
Heat Sink
Workflow
The workflow diagram below provides an overview of the example. The diagram shows the apps that you use as you perform the steps in sequence. Clicking a number in the diagram opens its corresponding step in the example.
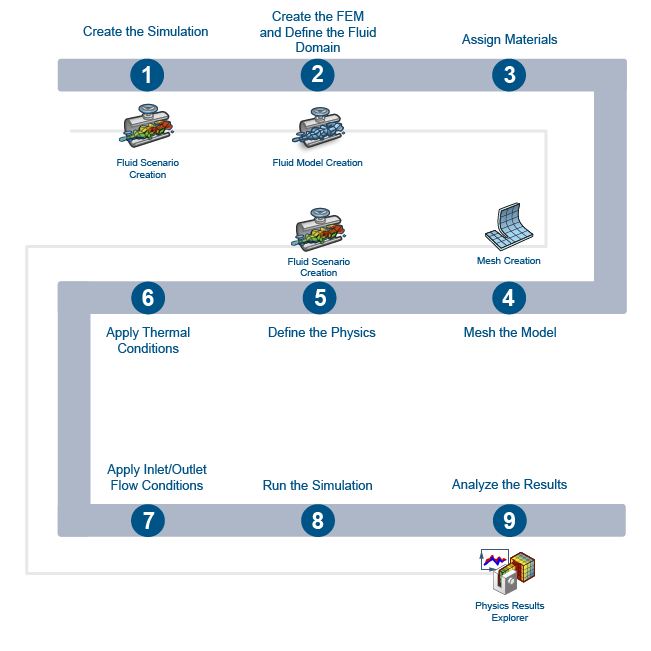
| Task | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create the Fluid Simulation | Create the simulation by first importing the model and material definitions into the 3DEXPERIENCE platform and then opening the model in the appropriate app. |
| 2 | Create the Fluid Domain | Use the fluid domain to define the volume in the model where the fluid is contained. |
| 3 | Assign Materials | Create a fluid section and two solid sections, and assign the corresponding materials. |
| 4 | Mesh the Model | Use a finite element model (FEM) representation of your geometry to perform the simulation. |
| 5 | Define the Physics | Define the physics for the fluid and solid, and use a static step to determine the nature and sequence of events in a simulation scenario. |
| 6 | Apply Thermal Conditions | Specify a contact interaction to define the thermal contact between the heat sink and the chip. Specify the chip as a volumetric heat source. |
| 7 | Apply Inlet/Outlet Flow Conditions | Apply a velocity inlet and pressure outlet to define the directions for the fluid flow in the model. |
| 8 | Solve the Simulation | Perform a simulation to solve for the effectiveness of the heat dissipation. |
| 9 | Review the Results | Display simulation data for the temperature distribution on the chip, heat sink, and air flow pattern using velocity vector plots and streamlines. |
Complete the workflow steps in the order in which they are listed. Deviation from the instructions associated with each step might cause model or scenario errors, which might prevent convergence of the simulation.