Disposing of a Defect Across a Model Version Hierarchy
Model version revisions can be affected by one or more defects that are reported against or identified in other model versions in their model version hierarchy. A Product Manager can use a disposition to indicate how a defect that affects a model version through its hierarchy is being disposed of, or mitigated, in that model version revision.
A model version revision can have only one disposition for each affecting defect. The disposition links the model version revision, defect, and any defect action used to resolve the defect in that model version revision. A disposition can be associated with only one defect action, because the defect action specifies how the defect is being disposed of, or mitigated, in a specific model version revision.
There are five types of dispositions available for defects:
| Disposition Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Errata | The defect is determined to be errata for this model version revision. The associated defect action's description and state are shown. |
| No Fix | There is no fix for the defect in this model version revision. |
| Not Impacted | This model version revision is not affected by the defect. |
| Spec Change | The defect is disposed of in this model version revision by changing the relevant product specification. |
| To Fix | The defect is to be fixed in this model version revision. The associated defect action's description, state, and committed model version are shown. |
| Important: If a disposition indicates that a model version in the hierarchy is "Not Impacted" by a defect, all model versions above that model version in the hierarchy (that is, they use the model version that is not impacted) are no longer considered to be affected by that defect either. That defect will no longer appear on the Affecting Defects reports for those model versions. The defect no longer needs a disposition for that model version or any of the model versions above that model version in the hierarchy. |
A model version revision can have many dispositions—one for each affecting defect. Because dispositions are created in the context of a defect and a model version revision, they are only listed in those contexts—there is no list of all dispositions that exist in the app.
Product Managers can create dispositions for their model version revisions that are affected by a defect reported against a model version in the hierarchy. In the following example, Defect 1 affects CHIP 1.1 through the RAM 1.5 model version in the hierarchy. The Product Manager of the CHIP model version uses Disposition 1 to dispose of Defect 1 in the CHIP 1.1 model version. Disposition 1 has a status of "No Fix," because the defect was not resolved in that model version revision. The relationship between Disposition 1, the CHIP 1.1 model version revision, and Defect 1 is shown shaded in yellow. Defect 1 will be fixed in the CHIP 1.2 model version revision, so the Product Manager uses a separate disposition, Disposition 2, with a status of "To Fix". Disposition 2 is linked to Defect Action 1, which will resolve the issue in CHIP 1.2, and to the affecting defect, Defect 1. This relationship is shown shaded in light blue.
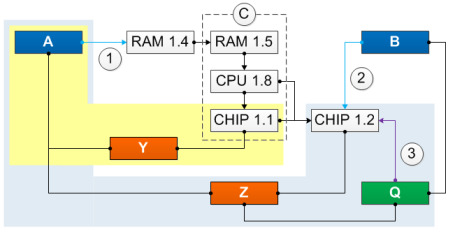
| Caption | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Defect 1 |
| B | Defect 2 |
| C | Model version hierarchy |
| Y | Disposition 1: No Fix |
| Z | Disposition 2: To Fix |
| Q | Defect Action 1 |
| 1 | Defect 1 was reported against RAM 1.4 |
| 2 | Defect 2 was reported against CHIP 1.2 |
| 3 | Defect Action 1 is committed to CHIP 1.2 |

